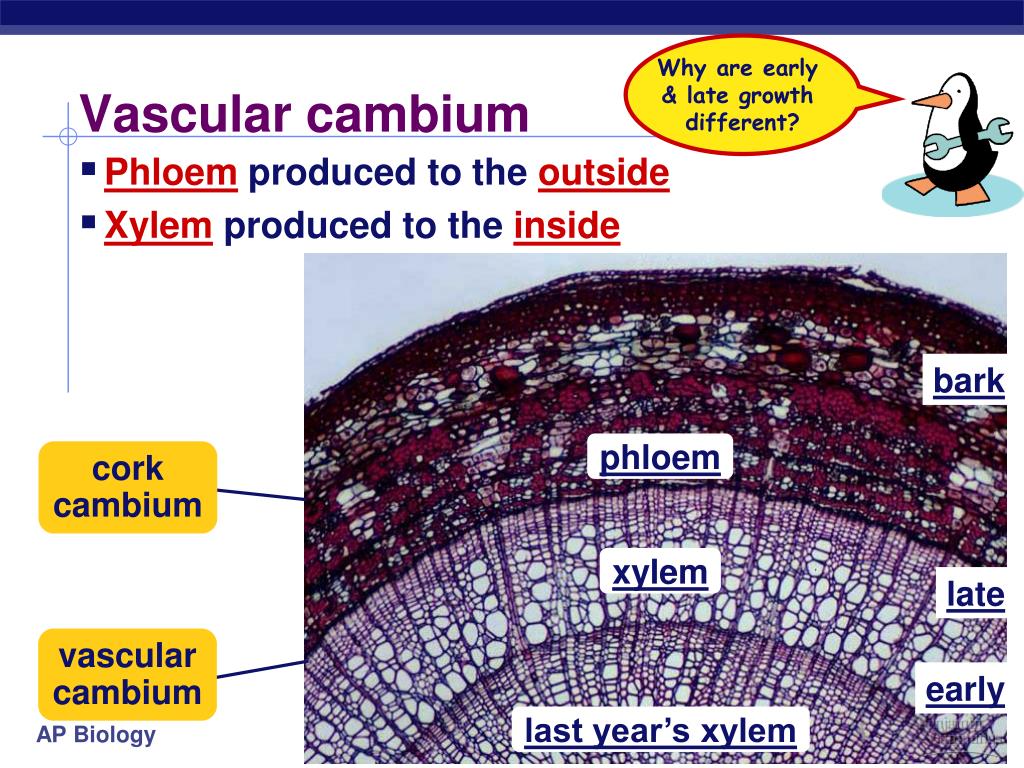
Cambium Causes Growth In . plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the stem or. the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the formation of secondary phloem and secondary xylem by. the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and.
from www.slideserve.com
in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the formation of secondary phloem and secondary xylem by. the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the stem or.
PPT Plant Growth PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID689168
Cambium Causes Growth In plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the formation of secondary phloem and secondary xylem by. vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the stem or. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium.
From slideplayer.com
Topic 9 Plant Biology. ppt download Cambium Causes Growth In the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the formation of secondary phloem and secondary xylem by. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From slidetodoc.com
Anatomy and Physiology Stems Student Learning Objectives Distinguish Cambium Causes Growth In cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From slideplayer.com
Designed by Pyeongsug Kim ©2009 SI Online (practice questions) Spring Cambium Causes Growth In cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDAssertion Cambium is a lateral meristem and cause growth in Cambium Causes Growth In lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.shaalaa.com
Discuss the Role of Cambium in Secondary Growth of Dicot Stems Cambium Causes Growth In in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From cronodon.com
Stem_Growth Cambium Causes Growth In the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From slideplayer.com
Informal Quiz Time Is it True or Is It False? ppt download Cambium Causes Growth In the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From xmind.app
Cambium Insight Guides Voslibert Xmind Cambium Causes Growth In the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the formation of secondary phloem and secondary xylem by. in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.researchgate.net
Cambium (CC) in Norway Spruce (Picea abies) at different phases; Aat Cambium Causes Growth In the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.pw.live
About Initiation And Activity Of Vascular Cambium Cambium Causes Growth In vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the stem or. cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium.. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.thedailygarden.us
Cambium The Daily Garden Cambium Causes Growth In the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.doubtnut.com
Differential activity of cambium causes light and dark bands of tissue Cambium Causes Growth In vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the stem or. in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From learning.uonbi.ac.ke
eXe Cambium Causes Growth In plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem).. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Cambium Root Cambium Causes Growth In vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the stem or. cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the formation of secondary phloem. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.alamy.com
Cambium tissue hires stock photography and images Alamy Cambium Causes Growth In vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (toward the center of the stem or root) and phloem (toward the outside of the stem or. the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the formation of secondary phloem and secondary xylem by. cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.alamy.com
Cambium hires stock photography and images Alamy Cambium Causes Growth In cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is. plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). . Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDCambium causes growth in (a) Circumference (b) Width (diameter Cambium Causes Growth In plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. the vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and. the thickening of the stem that occurs in secondary growth is due to the. Cambium Causes Growth In.
From www.researchgate.net
Role of hormones in plant growth and development Download Scientific Cambium Causes Growth In plants with secondary growth produce an additional lateral meristem, the cork cambium, that produces cells that form a new skin. lateral meristems include the vascular cambium and, in woody plants, the cork cambium (cambium is another term for meristem). in a dicotyledonous stem, the primary xylem and primary phloem are separated by cambium cells called intrafascicular cambium.. Cambium Causes Growth In.